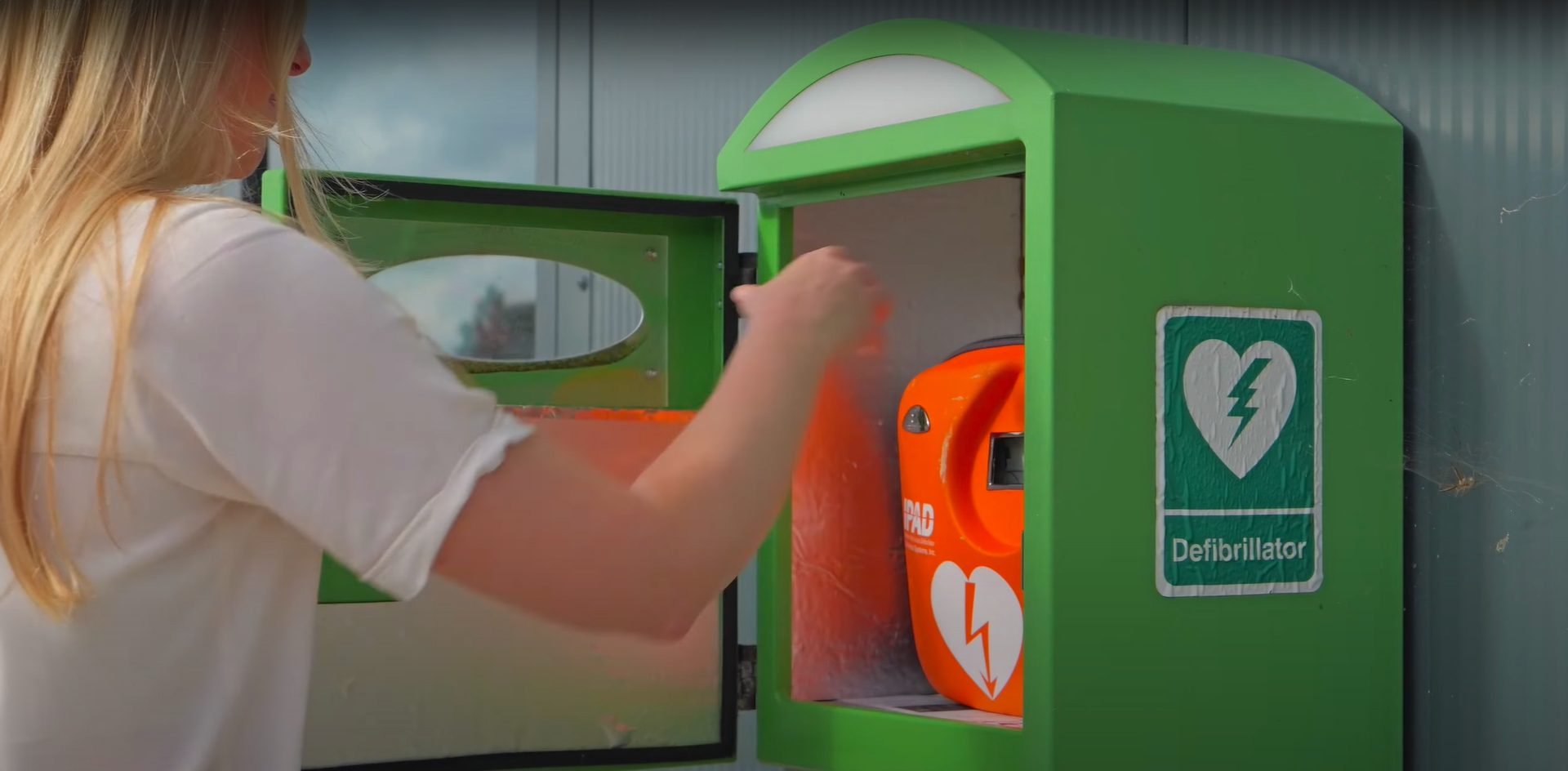
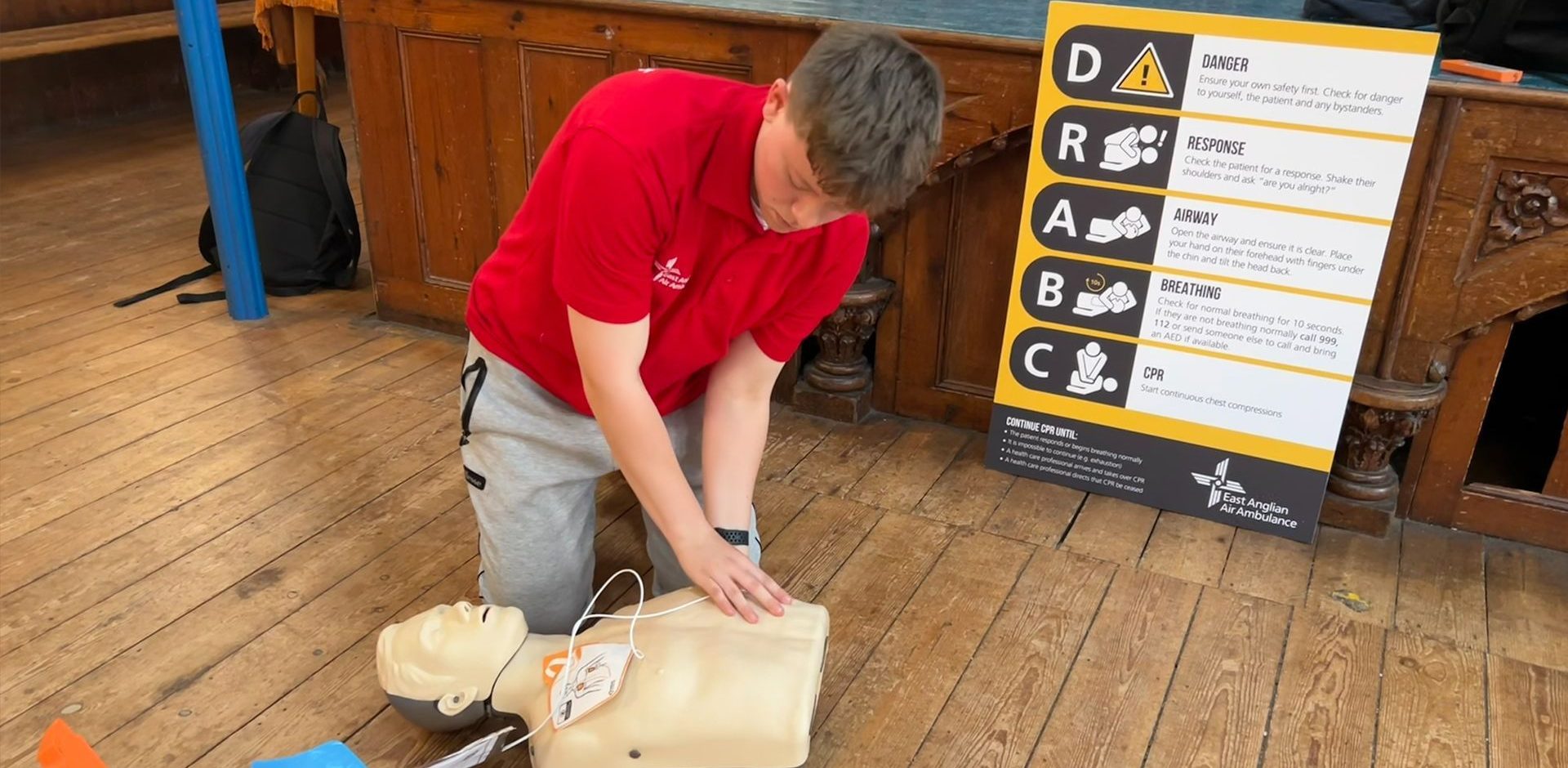
An AED (which may also be called a defibrillator or ‘defib’) works by analysing the heart to decipher whether the heart is in a shockable rhythm. The two shockable rhythms are known as Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (PVT).
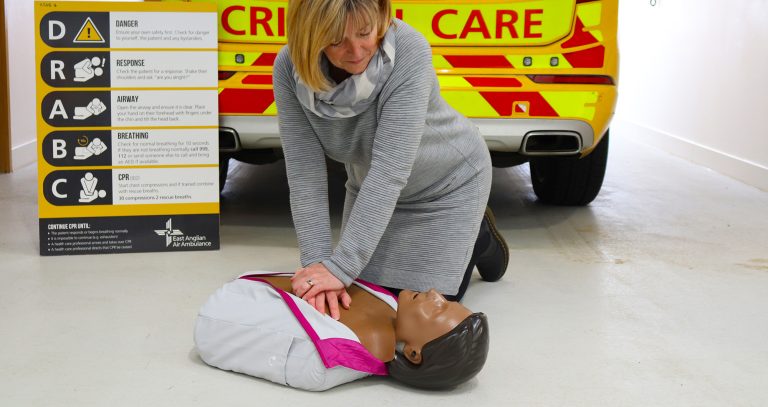
If the AED finds a shockable rhythm (VF or PVT), it will deliver a shock to the heart to stop the abnormal rhythm. Once the shock has been delivered, the AED will prompt the user to begin CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation).
A common misconception is that AEDs will shock no matter what, however, as above, the AED will only shock if it finds a shockable rhythm (VF or PVT). Therefore, if you are touching the casualty when the AED is analysing, it will say ‘no shock advised’, as the AED has potentially analysed your own heart and thus decided it does not need to be shocked. This is why it is important that when the AED says ‘stand clear’ you and anyone else in the environment, must not touch the casualty so that the AED can analyse effectively.